WHAT IS NEUROPATHY?
Neuropathy refers to the condition that affects the activity of nerves in your peripheral nervous system. This is a network of nerves that connects your brain and spinal cord, which are part of the central nervous system, to the rest of your body. This disorder is more widely called “peripheral neuropathy” because it influences many aspects of your body. The level of severity can differ with how many nerves your neuropathy is affecting. Peripheral neuropathy can damage one nerve or more. There are more than 100 types of peripheral neuropathy. Mononeuropathy, multiple mononeuropathy, and polyneuropathy are the three tiers of neuropathy that are possible. Carpal tunnel is also a subset of mononeuropathy. There are three types of nerve cells that revolve around this system. Sensory nerves, that carry messages made from your five senses from your spinal cord to your brain. Your peripheral nervous system connects the nerves from your brain and spinal cord to the rest of your body. This includes your arms, hands, feet, legs, internal organs, mouth, and face. The job of these nerves is to deliver signals back to your brain. Motor nerves, that carry message from the brain to your muscles for motor functions. And autonomic nerves are responsible for controlling body functions that occur outside our control, such as breathing, digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. The disorder neuropathy occurs when these nerve cells are damaged. When this happens, the normal way these cells communicate messages to the brain is disrupted and usually altered. This can happen with one or more of the nerve cell types.
DO I HAVE PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY?
Because there are different types of nerve cells, there are different types of peripheral neuropathy symptoms that all have different results. The disorder depends on the location and type of the nerve cells that are damaged. Neuropathy can be a slow or quick process, depending on the volume and type of nerve cells that are affected. Usually, peripheral neuropathy occurs in your feet or hands.
Sensory Neuropathy Symptoms ◆ Numbness and tingling. Particularly in your hands or feet. ◆ Changes in sensation, like severe pain or even a lack of being able to feel pain, pressure, temperature, or touch. ◆ Coordination loss. ◆ Burning sensations. ◆ Loss of reflexes. ◆ A feeling of wearing a layer like socks or gloves when you are not. ◆ Muscle weakness, particularly in your hands or feet.
MOTOR PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY SYMPTOMS
◆ Muscle fatigue and weakness. ◆ Difficulty walking or moving your arms or legs. ◆ Random muscle twitching. ◆ Cramps and spasms. ◆ Loss of muscle control and tone. ◆ Increase in clumsy behavior and frequent falling. ◆ Inability to move a part of your body.
AUTONOMIC PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY SYMPTOMS
◈ Increased or suddenly abnormal blood pressure or heart rate. ◈ Excessive sweating or sudden lack of ability to sweat. ◈ Problems with urinating. ◈ Sexual dysfunction. ◈ Heat intolerance. ◈ Diarrhea. ◈ Unintentional and sudden weight loss. ◈ Dizziness or fainting when standing up. ◈ Severe nausea or vomiting. ◈ Indigestion. Bowel or bladder issues.

The Details of Neuropathic Pain
Some sufferers of neuropathy can develop unusual triggers that can make them particularly sensitive to certain things because of heightened sensitivity (hypersensitivity) of the nerves to stimulation. For example, nerve sensitivity to touch can cause pain in some people with herpes; they can't tolerate clothing touching the infected area. Other nerve damage can result in painful body positions during standing or sitting. Nerve damage does not automatically mean you are going to suffer from nerve pain. Loss of feeling or numbness may occur in your affected area. Though it isn't painful, the numbness usually results in decreased sensitivity of the sense of touch that can interfere with dexterity in your hands. This can make activities like typing, tying shoes, or playing musical instruments arduous. Usually, nerve pain is worse at night, and as a result the individual can have fairly severe insomnia. This loss of sleep can cause additional issues so people with this type of nerve pain need to discuss the problem with their doctor to receive early treatment. Losing balance is another symptom of neuropathic pain. Numbness or loss of the sense of touch may be dangerous for the neuropathic sufferer because it directly affects balance and muscle strength. These symptoms can be combated by using things like braces, canes, or walkers. As we learned, some nerve damage may result in numbness instead of pain, but the numbness has the capability to mask damage to traumatized extremities like your feet. Individuals with this type of nerve damage can benefit by regularly examining their feet for possible injuries they cannot feel. Nerve pain is usually progressive, especially if the root cause is not treated. The usual progression of nerve pain is that it begins far away from your brain and spinal cord (hands and feet) and spreads backwards (retrograde) towards the arms and legs. With appropriate treatment, the progression may be halted or reversed.
What are the Methods of Diagnosing Neuropathy?
Exams and tests performed depend on the level of symptoms the neuropathy patient has. The diagnosis of neuropathy involves deep research through medical history and physical examinations to assist your health care examination, which tests your reflexes and function of sensory and motor nerves is an important component of your first examination. There are no specific blood tests that are specific for determining whether or not you have neuropathy. Since neuropathy is usually a subset of another disease, blood tests may be performed to see if you have one of the overarching conditions. Tests to determine your nerve function include: Electromyography (EMG) is a test that measures the function of the nerves. For this test, a very thin needle is inserted through the skin into the muscle. The needle contains an electrode that measures the electrical activity of the muscle. Nerve Conduction Velocity Test (NCV) measures the speed at which signals travel through the nerves. This test is often done with the EMG. In the NCV test, patches containing surface electrodes are placed on the skin over nerves in a variety of locations. The patches give off a gentle electrical pulse that stimulates the nerve. The electrical activity of the nerves is measured, and the speed of the electrical impulses between electrodes is calculated. -Nerve Biopsy is the surgical removal of a small piece of soft tissue to examine under a microscope. A pathologist, who is a physician specially trained in tissue diagnosis, examines the specimen and can help establish what caused your neuropathy. The procedure is performed using a local anesthetic.
WHO CAN GET NEUROPATHY?
Neuropathy is a more common disorder than people would like to admit. About 30% of Americans will be affected by neuropathy, and it occurs in over 60% of diagnosed people with diabetes. Diabetic neuropathy is a common type of neuropathy that occurs in people with diabetes, affecting their peripheral nerves due to high blood sugar levels. It is possible to develop neuropathy at any age, but the elderly is definitely at an increased risk. Men are more likely to develop neuropathy, as well as Caucasians. Neuropathy can also be an occupational hazard if your career requires you to participate in activities that make you use repetitive motions on a daily basis. There is a genetic predisposition for developing neuropathy. CMT disease, which is a combination of motor and sensory neuropathy, is an inherited disease that results in weakness in your lower legs and feet. The disorder can be so extreme that it can deform healthy feet. This makes it even more difficult to walk and causes clumsiness. The more common type of neuropathy is developed. There is a wide spectrum of causes of neuropathy. The most common is trauma. A sudden accident, injury, or fall can result in trauma to the peripheral nerves that ends in a pretty severe case of neuropathy. Infections and autoimmune disorders are also a common cause. Viruses and bacteria break down and damage nerve cells. HIV, the herpes virus, syphilis, and Lyme disease are a few examples of autoimmune diseases that can negatively affect nerve tissue. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and sensory loss. At times, neuropathy can be caused as a subset of a disease that has been happening to the entire body. Diabetes, cancers, kidney failures, bone marrow disorders and hormonal imbalances are all systemic diseases that can put you at a higher risk of developing neuropathy. Intensely strong medical techniques and prescriptions can damage peripheral nerves. Chemotherapy is a prime example of this. You can also develop neuropathy if your nerve cells are exposed to highly toxic substances like metal or industrial chemicals. Neuropathy can happen when blood cannot flow to your limbs because of inflammation, blood clots, or other circulation complications. When your blood flow is decreased, your nerve cells do not receive enough oxygen and essentially suffocate. Nerve damage and nerve cell death are extremely likely in this case. Excessive use of alcohol can neglect the body of needed thiamine or other essential nutrients. Due to malnourishment, nerve cells can become damaged or die.
HOW CAN I TREAT PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY?
Lifestyle Changes
Any lifestyle habits that support your nerve health will decrease the symptoms or chance of developing peripheral neuropathy and improve peripheral neuropathy treatment outcomes. ● Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins to keep your nerves healthy. Since not having the required vitamins is such an issue when it comes to neuropathy, it is important to combat these effects by ensuring your body has all the nutrients it needs. ● Regular exercise. 30 minutes to an hour of exercise with determined stretching will greatly help you to have more balance and control in your body. ● Cutting out activities that could result in nerve damage or irritation. Quitting your job that requires you to make repetitive motions or exposes you to toxic chemicals can assist you in lowering your neuropathy development. ● Cutting out smoking or excessive alcohol use will help your body establish a healthy medium and reduce the number of things it must fight off.
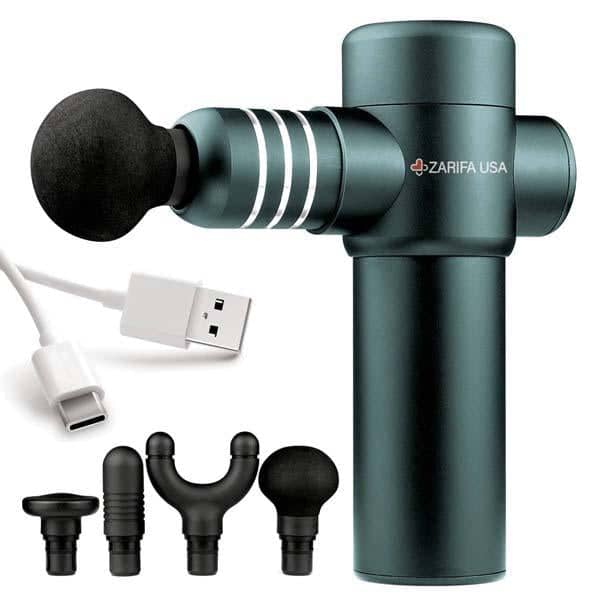
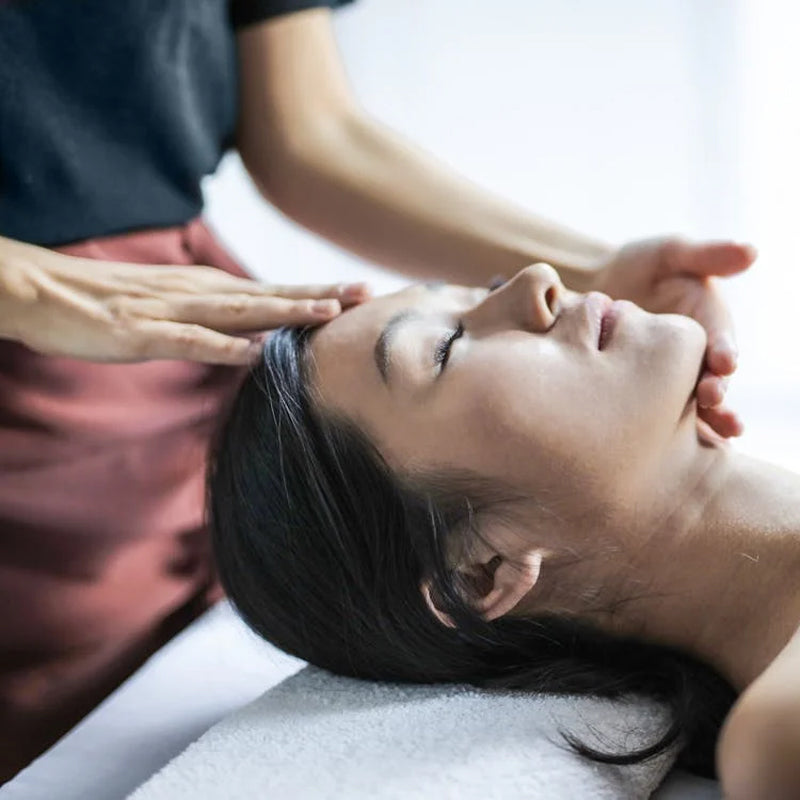
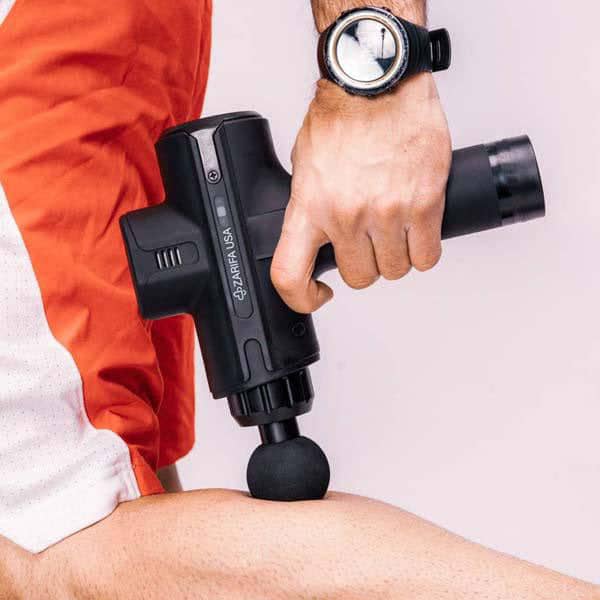
Medications and Therapies● Pain relievers. NSAIDs or other over-the-counter pain medications can relieve mild symptoms of neuropathy. For more severe feeling symptoms you may need your doctor to prescribe you something stronger. It is important to note addiction to these medications is a credible situation, and to double check what your case needs with your doctor to not cause additional damage. ● Anti-seizure medications may relieve some of the lasting nerve pain. These prescriptions were created to treat epilepsy and can negate some of the similar symptoms in neuropathy. ● Antidepressants. Surprisingly, the pain numbing affects of antidepressants have been found to relieve pain by altering the chemical processes in your brain and spinal cord. This disruption can interfere with the process that causes you to feel pain and can decrease neuropathy symptoms significantly. ● Acupuncture. Targeting various points on your body with thin needles may reduce your neuropathy symptoms. It may take a few sessions before you can see significant improvement, but there have been cases that report noteworthy progress. ● Massage and Electrical Stimulation Therapies
Treating peripheral neuropathy often involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and physical therapies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. You can receive massage treatment that will assist with neuropathy symptoms in a cleansing day spa, treatment room at a physical therapy clinic, or even in the comfort of your own home using massage tools that help with neuropathy. Massage therapies help soothe sore and inflamed joints and muscles in ways that medication often cannot. Peripheral neuropathy patients have reported lessened stress levels and better sleep when staying on a continuous massage schedule. Massage therapies are the most popular secondary therapies used by Americans (9% as reported by the NCCAM). Research suggests that massage affects your internal body balance by promoting beneficial blood pressure, heart rate, hormones, and other vital and immune system signals. “Regular massage of muscles and joints, whether by a licensed therapist at a spa or by self-massage at home, can lead to a significant reduction in pain,” stated Tiffany Field, Ph.D., and Director of the Touch Research Institute. Throughout her studies Field found that simple massage therapy led to pain improvement, reduced joint stiffness, reduced joint inflammation, and overall heightened joint performance. A decrease in the stress hormone cortisol, a boost of serotonin production, and general mood improvement are just a few of the results of massage therapy in neuropathy patients. Seeing as a large percentage of pain is emotional, and the stress hormone cortisol is reduced, pain levels in these patients were lowered. You can receive massage chronic pain relief at a day spa, a therapeutic massage clinic, or at home massage.