Arthritis and Circulation: The Impact of Your Joints and Exercise
Getting appropriate amounts of exercise and developing a healthy lifestyle are necessary in the battle against arthritis. Most people that are at a risk for developing arthritis are obese or overweight, and some are merely unaware if exercising and placing stress on the joint would benefit their joint health. You would think that increased movement would damage your already sore joints. So how would increasing use of the damaged joint help?
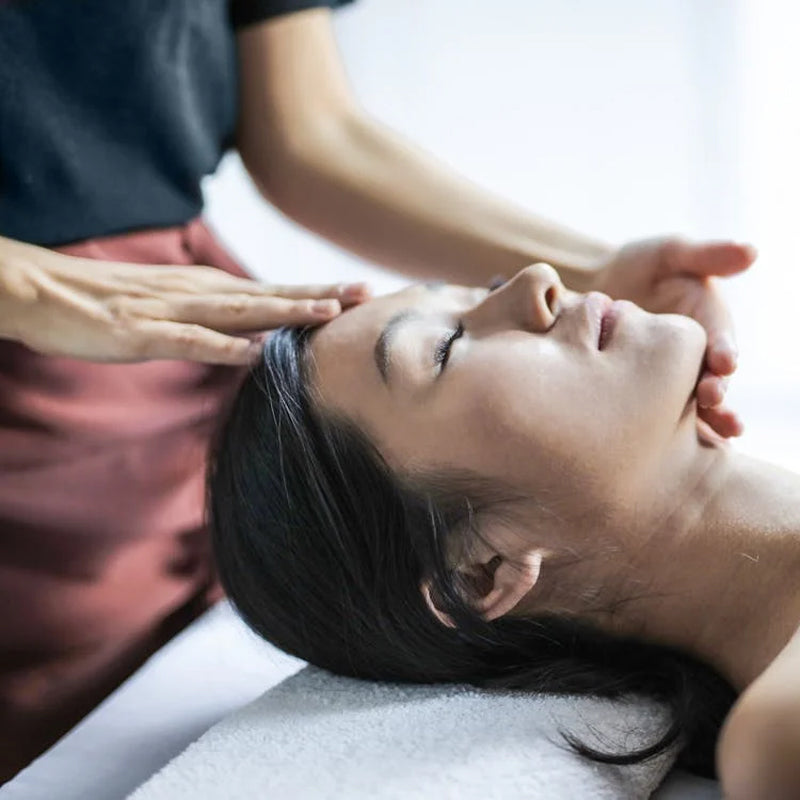
In addition to exercise, massage therapy can also help manage arthritis symptoms by relieving pain and stiffness, improving movement, and easing chronic inflammation.
UNDERSTANDING ARTHRITIS AND CIRCULATION
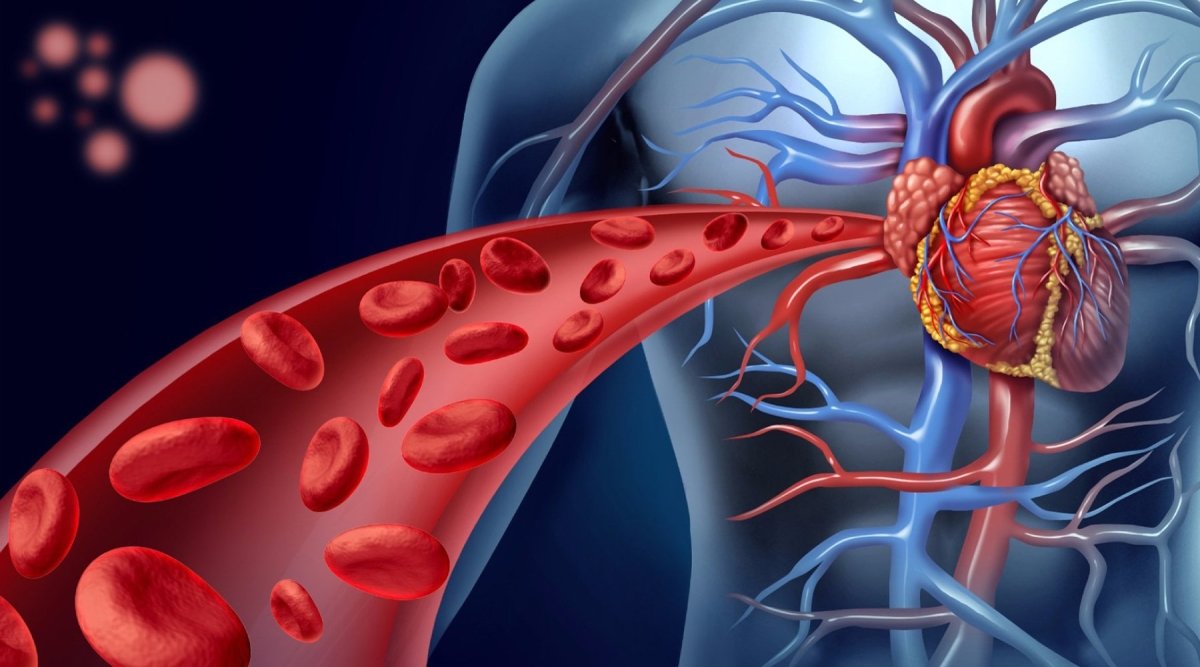
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is more than just a joint disease; it’s a chronic inflammatory condition that can significantly impact your blood vessels and overall circulation. When inflammation occurs in the joints, it can also affect the blood vessels, leading to a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. This is because the same inflammatory processes that cause joint pain and swelling can also cause blood vessels to become inflamed, narrowed, or even blocked.
Blood vessels are crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to your joints, and when they are compromised, it can disrupt this essential process. This disruption can exacerbate joint pain and stiffness, making it even more challenging to manage RA symptoms. Moreover, chronic inflammation associated with RA increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes.
Understanding the link between arthritis and circulation is vital for managing RA effectively. By being aware of how RA affects your blood vessels, you can take proactive steps to reduce cardiovascular risk factors and improve your overall health. This includes regular monitoring of your heart health, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and working closely with your healthcare provider to manage both your RA and cardiovascular health.
UNDERSTANDING RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints. This leads to inflammation and damage, which can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. But RA doesn’t just stop at the joints; it can also affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, and blood vessels. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options of RA is crucial for managing the condition and preventing complications, including those related to vascular health. By staying informed, you can take proactive steps to manage your symptoms and maintain a better quality of life.
INCREASED BLOOD FLOW AND CIRCULATION
It’s the obvious answer, but exercise gets everything moving! Blood gets pumping even more throughout your body when you exercise, even in your swollen joints. The tissue then can get the nutrients and fresh oxygen it needs to promote healing and improved activity. Increased blood flow also helps reduce inflammation, which is a common issue for those with arthritis. By keeping the blood circulating, exercise helps to flush out inflammatory substances from the joints and surrounding tissues, reducing pain and stiffness over time, providing pain relief. Additionally, increased blood flow from exercise can help reduce heart disease risk, especially for those with rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, increased blood flow from exercise can help reduce heart disease risk and improve arterial health, especially for those with rheumatoid arthritis.
THE CELLULAR TRASH GETS TAKEN OUT
Physical activity triggers a biological process known as autophagy, which is your body identifying damaged cells as unnecessary. Once your body decides that these “floating” cells are garbage, it disposes of them through continual blood circulation. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy joint function and preventing further damage. Autophagy helps clear out the cellular debris that can accumulate in joints, reducing the risk of inflammation and joint pain. Regular exercise, therefore, not only helps in managing symptoms but also in maintaining the overall health of your joints and cellular health.
REBUILDING CARTILAGE WALLS
Though the cause is unknown, observational research shows that even through degenerative joint disease, patients can see their cartilage walls be rebuilt when they exercise regularly. Cartilage is the hardest tissue surrounding the joint, and having a solid cartilage wall will enable you to exercise more and more frequently after a duration of time, promoting cartilage regeneration. Strengthening the cartilage can significantly improve joint function and reduce pain. Exercises that involve gentle, weight-bearing activities, such as walking or swimming, can stimulate the production of new cartilage cells, promoting joint health and flexibility. Additionally, deep tissue massage can help in rebuilding cartilage and improving joint function by addressing severe tension or pain in the muscles and connective tissues.
JOINT MUSCLE BUILD
When the tissues and muscles surrounding the joint are strong, they protect and cushion the weak joints, contributing to overall muscle strength. Ligaments and tendons also build up strength and contribute to the healthy cocoon that surrounds the affected joint. Much like rebuilding the cartilage walls, muscle is another tissue that can securely protect your body when suffering from arthritis. Reducing muscle tension through massage can help in building joint muscle, as it improves circulation and flexibility. Strong muscles help absorb the shock and stress placed on joints during movement, reducing the risk of injury and pain. Incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can help build and maintain muscle mass, providing better support for your joints.
GENERATED SYNOVIAL FLUID
The synovial membrane surrounds all your joints, and it produces a smooth fluid that allows your bones to move around each other effortlessly. Usually, if you have a degenerative joint disease, this fluid lessens and can cause an arthritis flare-up. Physical activity promotes movement of the synovial fluid that lubricates your joints and results in less chronic pain for you, enhancing joint lubrication. Regular movement helps keep this fluid circulating, ensuring that your joints remain well-lubricated and function smoothly. This lubrication reduces friction between the bones, minimizing pain and preventing further joint damage. Additionally, hot stone massage can help in promoting the movement of synovial fluid and reducing chronic pain.
EXERCISE AND BLOOD FLOW
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of managing rheumatoid arthritis, particularly when it comes to maintaining healthy blood flow and reducing inflammation. Engaging in physical activity helps to pump blood more efficiently throughout your body, including your swollen joints, which can aid in delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the tissues. This increased blood flow not only promotes healing but also helps to flush out inflammatory substances, reducing pain and stiffness over time.
Aerobic exercises, such as walking or cycling, are particularly beneficial for improving cardiovascular health and enhancing blood flow. These activities help keep your heart and blood vessels in good shape, reducing the risk of heart disease, which is a common concern for RA patients. Additionally, resistance training can strengthen the muscles around your joints, providing better support and stability, which can help prevent injuries and reduce inflammation.
Incorporating a variety of exercises into your daily routine can significantly improve your RA symptoms and overall health. Whether it’s a brisk walk, a gentle yoga session, or a swim, regular physical activity can help you manage your condition more effectively and lead a healthier, more active life.
IMPACT OF EXERCISE ON BLOOD CIRCULATION AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
Blood circulation is crucial to attaining the highest quality of lifestyle when diagnosed with a degenerative joint disease like arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis has been proven to block blood flow in body parts like arms, legs, and elbows. The reduced blood flow can lead to coronary artery disease, inflammation, and narrowed veins. These complications create heart conditions that are chronic, inflamed, and damaging to blood vessels, contributing to cardiovascular disease and other vascular complications. This puts arthritis patients at more of a risk for heart attack, stroke, heart disease, and even heart failure.
It is important for rheumatoid arthritis patients to monitor their heart health and be vigilant about symptoms like chest pain, promptly reporting them to their healthcare providers.
Regular exercise helps improve cardiovascular health by increasing blood flow and reducing inflammation throughout the body. It helps keep the arteries flexible and clear of plaque, reducing the increased risk of heart-related complications. For arthritis patients, maintaining good cardiovascular health is essential to manage both joint and heart health effectively. Exercise can lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and enhance overall heart function, contributing to a healthier and more active lifestyle. Additionally, seeking help from a licensed massage therapist can provide comfort to aching muscles, reduce stress, and improve movement, which is beneficial for managing arthritis symptoms. Understanding the vascular implications for rheumatoid arthritis patients is crucial to improving patient outcomes and reducing the risks associated with cardiovascular disease.
MANAGING INFLAMMATION THROUGH EXERCISE
Exercise is a cornerstone in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation, improve joint mobility, and strengthen muscles, making it easier to perform daily tasks. Moreover, exercise can help mitigate cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which are common in RA patients. Aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent for improving cardiovascular health, while strength training exercises can help build muscle and enhance joint stability. By incorporating a balanced exercise routine, you can manage your RA symptoms more effectively and improve your overall health.
TYPES OF EXERCISES BENEFICIAL FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
Low-impact exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals with arthritis. These exercises are gentle on the joints and help improve strength, flexibility, and overall fitness without causing further damage. Some recommended low-impact exercises include:
- Swimming: Water supports your body, reducing stress on the joints while allowing you to move freely. Swimming and water aerobics can help improve cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and joint flexibility. However, rheumatoid nodules may still develop at pressure points despite the benefits of swimming.
- Walking: A simple and effective way to improve cardiovascular health and strengthen the muscles around your joints. Walking can be easily incorporated into your daily routine and adjusted to your fitness level.
- Yoga: Focuses on gentle stretching and strengthening exercises that enhance flexibility, balance, and relaxation. Yoga can also help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Cycling: Provides a cardiovascular workout without putting too much stress on the joints. It helps strengthen the muscles in the legs and improve overall fitness.
- Strength Training: Using resistance bands, light weights, or body-weight exercises can help build muscle strength, which supports and protects your joints.
Additionally, moderate pressure in massage therapy for arthritis is important as it stimulates pressure receptors under the skin, conveying signals to the brain that alleviate pain and release stress-reducing neurochemicals like serotonin.
CREATING AN EXERCISE PLAN FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Creating an exercise regimen for RA requires careful consideration of your fitness level, joint mobility, and overall health. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a physical therapist to develop a personalized exercise plan that suits your needs. Your plan should include a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid exacerbating joint pain and inflammation. Remember, consistency is key, and a well-rounded exercise plan can significantly improve your quality of life.
COMMON EXERCISE MISTAKES TO AVOID
When exercising with RA, it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes that can worsen joint pain and inflammation. Overexerting yourself can lead to increased joint pain and inflammation, so it’s important to listen to your body and take regular breaks. Ignoring joint pain and continuing to exercise can cause further damage, so always pay attention to how your body feels. Not warming up or cooling down properly can lead to muscle strain and joint injury, so make sure to include these steps in your routine. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can exercise safely and effectively, ensuring exercise safety.
TIPS FOR EXERCISING WITH ARTHRITIS FOR PAIN RELIEF
- Warm-Up and Cool Down: Always start with a gentle warm-up to prepare your joints and muscles for exercise. Finish with a cool-down period to gradually lower your heart rate and stretch your muscles.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise. If you experience increased pain or discomfort, adjust your routine or try a different activity.
- Stay Consistent: Regular exercise is key to managing arthritis symptoms and improving joint health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
- Modify Exercises: Adapt exercises to your comfort level and ability. Use support or assistive devices if needed, and avoid high-impact activities that could strain your joints.
- Consult Professionals: Work with your doctor, physical therapist, or a certified fitness trainer to develop a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your needs and abilities.
- Massage for Arthritis: Consider incorporating different types of massage for arthritis, such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, or myofascial release. These techniques can improve circulation, relieve pain, and ease tension related to arthritis.
- Monitor for Complications: Be aware of rare but serious complications like rheumatoid vasculitis, an inflammatory condition affecting blood vessels that can lead to organ damage. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent permanent tissue damage.
Exercise is a powerful tool in managing arthritis and improving joint health. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can increase blood flow, promote autophagy, rebuild cartilage, strengthen muscles, and enhance the production of synovial fluid. These benefits contribute to reduced pain, improved joint function, and better overall health. Remember to choose low-impact exercises, stay consistent, and seek professional guidance to maximize the benefits of your exercise routine. With the right approach, you can maintain a healthy, active lifestyle and manage your arthritis effectively, contributing to better pain management.
Please consult your doctor or physical therapist when deciding what exercise plan would work best for you in your specific arthritis situation.
MONITORING PROGRESS AND STAYING MOTIVATED
Monitoring your progress and staying motivated are essential for maintaining a consistent exercise routine with RA. Track your progress, set realistic goals, and celebrate small victories to keep yourself motivated. Finding an exercise buddy, joining a support group, or working with a personal trainer can also help you stay on track. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider can help monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your exercise plan. By staying motivated and tracking your progress, you can achieve your fitness goals and manage your RA symptoms more effectively, ensuring exercise adherence.
OVERCOMING EXERCISE BARRIERS
Exercise barriers are common in RA patients, but they can be overcome with the right strategies. Joint pain, fatigue, and lack of motivation are common challenges, but breaking exercises into smaller, manageable chunks can make them more achievable. Finding low-impact exercises that are gentle on the joints, such as swimming or yoga, can also help. Schedule your workouts at times when your energy levels are highest, and choose exercises that you enjoy to make them more engaging. Working with a healthcare provider or physical therapist can help you develop a personalized exercise plan that addresses your specific needs and challenges. By overcoming these barriers, you can maintain a consistent exercise routine and improve your overall health, utilizing exercise modifications as needed.
THE IMPACT OF ARTHRITIS ON BLOOD VESSELS
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) doesn’t just affect your joints; it can also have a significant impact on your blood vessels. Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of RA, can cause blood vessels to become narrowed or even blocked, restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues. This restricted blood flow can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
One rare but serious complication of RA is rheumatoid vasculitis, an inflammatory condition that affects the blood vessels. Rheumatoid vasculitis can lead to further damage and significantly increase cardiovascular risk. Early diagnosis and treatment of RA are crucial in preventing or slowing the progression of blood vessel damage. By managing RA effectively, you can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and maintain better overall health.
SELF-CARE FOR ARTHRITIS MANAGEMENT
Self-care is a cornerstone of managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and preventing complications. Regular exercise, such as yoga or swimming, can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. These low-impact activities are gentle on the joints while providing significant benefits for your overall health.
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can also be beneficial. Reducing stress and anxiety can have a positive impact on your RA symptoms.
Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy weight are also essential components of self-care. Adequate rest helps your body repair and rejuvenate, while a healthy weight reduces the strain on your joints. By focusing on these self-care strategies, you can manage your RA symptoms more effectively and improve your quality of life.
LIVING WITH ARTHRITIS
Living with rheumatoid arthritis requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond medication. It involves making lifestyle changes and adopting self-care practices that can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. One of the key aspects of managing RA is reducing stress and anxiety, as these can exacerbate inflammation and worsen symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can be incredibly beneficial in managing stress levels.
A balanced diet is another crucial component of RA management. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, can help reduce inflammation and promote joint health. Foods like fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and colorful fruits and vegetables should be staples in your diet.
Getting enough sleep is also essential, as it allows your body to repair and rejuvenate. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help manage your RA symptoms. Additionally, staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can empower you to make informed decisions about your care. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and staying up-to-date with new developments in RA treatment can help you manage your condition more effectively.
By focusing on these self-care strategies, you can take control of your RA and improve your overall well-being. Remember, managing RA is a continuous journey, and adopting a comprehensive approach can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION
Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and preventing complications. If you experience chest pain or shortness of breath, seek medical attention immediately, as these could be signs of a serious cardiovascular issue.
If you notice new or worsening symptoms, such as increased joint pain or swelling, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. Additionally, if you experience numbness or tingling in your hands or feet, or if you have a fever or chills, seek medical attention promptly.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your RA and making necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. By staying vigilant and proactive about your health, you can manage your RA more effectively and reduce the risk of complications.